FAQ
MISCELLANEOUS TERMS:
Steel Melting Scrap :
Steel waste/scrap not usable as such in its existing form which are further re-melted to produce liquid steel to produce various products. Depending on their form/type, they are classified as Heavy Melting Scrap, Light Melting Scrap, Turnings/borings etc.Re-rollable Scrap :
Seconds & defective products, cuttings/end cuttings, used steel products like used rails etc which could be directly used for re-rolling (without resorting to re-melting) into finished products for specified applications. These are substitutes of steel billets /pencil ingots. Ship breaking generates substantial quantity of re-rollable steel scrap.Integrated Steel Plants :
Steel plants using iron ore as the basic raw material for production of crude steel which is further rolled into finished shapes in-house. Conventionally, these plants have captive coke ovens also and the sensible heat of the outgoing gases from iron/coke making are utilised as fuel for various applications. It therefore, includes units with in-house coke making (optional), iron making followed by production of liquid steel & crude steel and finished steel. So all ISPs adopting BF- BOF route and Major producers adopting Corex-BOF or DRI-EAFor MBF-EOF technology would technically, fall under this category.Mini Steel Plants :
Conventionally, EAF/IF based steel plants with/ without captive rolling mills were covered under this category. However, now all steel plants (based on any technology) of capacity upto 5 lakh tpa are covered under this category.Primary Steel Producers :
Steel (crude and/or finished steel) producers using iron ore as the basic raw material/input. It therefore, includes in-house iron making followed by production of liquid steel & crude steel with/without in-house rolling. So, all ISPs adopting BF- BOF route and Major producers adopting Corex – BOF or DRI-EAF or MBF-EOF technology would fall under this category.Hot Rolling :
Rolling of steel at above the recrystallisation temperature of steel (normally above 1000 C) to produce Hot Rolled Long products/Flat Products from semis. Ingots are also hot rolled to get semis. At times blloms are also hot rolled to produce billets. Rolling Mills used for hot rolling are known as Hot Rolling Mills.Cold Rolling :
Rolling of steel (normally flat products) below the recrystallisation temperature of steel (normally at room temperature) to produce cold rolled sheets /strips /coils. Mills used for the purpose are called Cold Rolling Mills.2Hi/4 Hi/6 Hi/20 Hi Mills :
Rolling Mills are classified as 2-High / 2 Hi, 4 Hi and so on depending on Number of Rolls used in the arrangement/configuration of rolls in single stand. For example, a 2 Hi mill consist of 2 rolls one above the other known as upper roll and the lower roll. In a 4 Hi mill, there are 4 rolls in a stand—2 upper rolls one above the other and 2 lower rolls one above the other.| Sl | Characteristic | Arc Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Operating Principle | 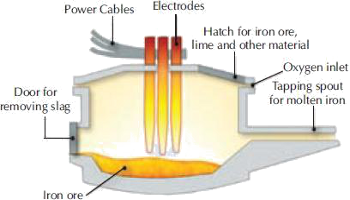 The arc forms between the charged material and the electrode by short-circuit between the electrodes and raw materials which causes high-temperature electric arc to melt raw materials The arc forms between the charged material and the electrode by short-circuit between the electrodes and raw materials which causes high-temperature electric arc to melt raw materials |
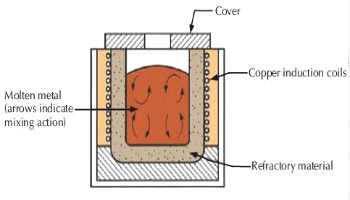 Induction Furnace heating is accomplished through induction i.e. heating an electrically conducting object (usually a metal) by Electro magnetic Induction where eddy current is generated within the metal and resistance leads to Joule Heating of the metal. An Induction Furnace uses induction to heat metal to its melting point. Induction Furnace heating is accomplished through induction i.e. heating an electrically conducting object (usually a metal) by Electro magnetic Induction where eddy current is generated within the metal and resistance leads to Joule Heating of the metal. An Induction Furnace uses induction to heat metal to its melting point. |
| 2 | Refining Capability | (A). Slag is removed automatically. (B). Precision control of chemistry of the molten metal. (C). S & P removal capacity is very good. | (A). Slag is removed manually. (B). Control of chemistry of the molten metal is not good i.e. lack of refining capacity. (C). Removal of S & P is limited. |
| 3 | Operating Temperature | High operating temperature | Operating temperature is lower than Arc Furnace |
| 4 | Dissolved Gas | Low content of dissolved gases in molten metal. | Content of dissolved gas in molten metal is more than Arc Furnace. |
| 5 | Reduction in Specific Energy | Large reduction in specific energy (energy per unit weight) required to produce the steel | Large reduction in specific energy (energy per unit weight) to produce the steel is not possible in Induction Furnace. |
| 6 | Starting or stopping the Furnace | Arc Furnace can rapidly start and stop, allowing the steel mill to vary production according to demand. | Induction Furnace cannot start or stop rapidly. |
| 7 | Life of Refractory lining | Life of Refractory lining is more than Induction Furnace. | Life of Refractory lining is comparatively lower than Arc Furnace. |
| 8 | Variety of Steels | Possibility of producing variety of steels. | Variety of steels cannot be produced. |
| Sl | Integrated Steel Plant | Ordinary Re-Roller |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manufacturing flow chart process: Iron Ore ?DRI ? SMS ? CCM (Billet Plant) ? RM ? TMT TMT Route ? TMT Re-bar Ingot produces from Route ? TMT Re-bar | Manufacturing flow chart process: Ingot ? RM ?TMT Route ? TMT Re-bar Ingot produces from different type of steel scrap ? SMS ? Ingot . |
| 2 | Integrated Steel Plant conforms the consistency in quality product | Ordinary Re-Roller cannot conform the consistency in quality product. |
| 3 | Chemical properties of billet top, middle & bottom portion all are same. Shape of billet is square | Chemical properties of ingot top, middle & bottom portion are different types. Shape of ingot is taper. |
| 4 | Continuous casting billet is a very minor casting defect in respect of ingot | Ingot is another harmful defect such as center piping, blow hole, cracks & inclusions etc. This has a very bad effect in rolling product. |
| 5 | Achievement of proper levels of sulphur & phosphorus is a process of capability inherent to the iron ore based integrated steel making route. As per Indian Standard (IS 1786) calls for sulphur & phosphorus content of 0.060% max. each for the Fe 415 grade with further provision that S&P added together would not exceed 0.110%. | Major Re-rollers/Ingot producers are unable to meet even these relaxed standard consistently. |
| 6 | Complete automation TMT route can produce the desired yield strength with steel of relatively lower carbon equivalent by adjusting the on line Q& T parameters. IS :1786 limits the carbon content to 0.25% max. & CE to 0.42% max. for guaranteed weldability. The average carbon content maintained by Shyam Steel Industries Limited is 0.19% with a standard deviation of 0.03% across all sections. | Re-roller neither maintains adequate TMT route and chemical composition of material nor maintains a specific range since they are using an Ingot. |
| 7 | Good Thermex TMT Re-bars ensure the Re-bars with a uniform and concentric hardened tempered Martensite periphery and the softer Ferrite-Pearlite core. | Major Re-rollers producing TMT Re-bars do not ensure that the Re-bars have a uniform and hard periphery signifying the quenching has not taken place all round the periphery. Rolling mill production system is either manual or semi automatic & mill personnel are not fully trained in quenching & tempering technology. |
| Sl | Ingot | Billet |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | In Ingot casting, the liquid steel flows through a refractory channel & fills up cast iron mould under static condition from one side. This process has certain deficiencies. Like:- Refractory particles chip-off from the channel and get mixed with liquid steel thereby causing undesirable inclusions in Ingot leading to rolling defect. | In continuous casting technology liquid steel flows from furnace to caster through a copper mould. The water in the mould gets cooled and oscillates at a predetermined rate. The oscillation, cooling and pausing is done in such a controlled condition that the liquid steel solidifies into equiaxed crystals. |
| 2 | The liquid steel during the solidification process releases gas which gets entrapped in the steel and form blowholes and cavities in Ingot. | The gas in liquid steel escapes during solidification owing to continuous casting technology. |
| 3 | Owing to the process of solidification segregation of chemical alloys takes place. The chemical properties vary at different portions of Ingot. | In billet owing to continuous casting chemical alloys are uniformly spread. |
| 4 | In Ingot very harmful defects such as center piping, blow hole, cracks & inclusions etc. are found. | In continuous casting, no centre piping blow hole, crack or inclusion is formed. |
| 5 | The surface of Ingot develop scabs and laps due to pouring defects on account of bad mould surface. | The surface of billet is clear with no scabs and laps due to smooth copper mould surface. |
| 6 | TMT Re-bars rolling from Ingots suffer from deficiency in tensile properties and there is inconsistency in tensile strength and elongation. | TMT Re-bars produced from continuous casting billets show high tensile strength and elongation and there is remarkable consistency of properties. |
| 7 |  |
 |
Details of different Codes and Standards of rolling
product for various requirements are as follows:
A. Raw Material
IS 2830/1992 : Carbon steel cast billet, ingots, blooms and slabs for rerolling into steel for general structural purpose.
IS 2831/2001 : Carbon steel cast billet, ingots, blooms and slabs for rerolling into low Tensile Structural steel for general structural purpose.
IS 10812/1992 : Specification for Sponge iron.
B. TMT Re-Bars / HYSD Bars
IS 1786 / 2008 (Fe 415 / Fe 415D / Fe 500 / Fe 500D /Fe 550 / Fe 550D / Fe 600):
Specifications for High Strength Deformed Steel Bars (TMT Bars) & Wires for concrete re-enforcements.
MISCELLANEOUS TERMS:
Steel Melting Scrap :
Steel waste/scrap not usable as such in its existing form which are further re-melted to produce liquid steel to produce various products. Depending on their form/type, they are classified as Heavy Melting Scrap, Light Melting Scrap, Turnings/borings etc.
Re-rollable Scrap :
Seconds & defective products, cuttings/end cuttings, used steel products like used rails etc which could be directly used for re-rolling (without resorting to re-melting) into finished products for specified applications. These are substitutes of steel billets /pencil ingots. Ship breaking generates substantial quantity of re-rollable steel scrap.
Integrated Steel Plants :
Steel plants using iron ore as the basic raw material for production of crude steel which is further rolled into finished shapes in-house. Conventionally, these plants have captive coke ovens also and the sensible heat of the outgoing gases from iron/coke making are utilised as fuel for various applications. It therefore, includes units with in-house coke making (optional), iron making followed by production of liquid steel & crude steel and finished steel. So all ISPs adopting BF- BOF route and Major producers adopting Corex-BOF or DRI-EAFor MBF-EOF technology would technically, fall under this category.
Mini Steel Plants :
Conventionally, EAF/IF based steel plants with/ without captive rolling mills were covered under this category. However, now all steel plants (based on any technology) of capacity upto 5 lakh tpa are covered under this category.
Primary Steel Producers :
Steel (crude and/or finished steel) producers using iron ore as the basic raw material/input. It therefore, includes in-house iron making followed by production of liquid steel & crude steel with/without in-house rolling. So, all ISPs adopting BF- BOF route and Major producers adopting Corex – BOF or DRI-EAF or MBF-EOF technology would fall under this category.
Hot Rolling :
Rolling of steel at above the recrystallisation temperature of steel (normally above 1000 C) to produce Hot Rolled Long products/Flat Products from semis. Ingots are also hot rolled to get semis. At times blloms are also hot rolled to produce billets. Rolling Mills used for hot rolling are known as Hot Rolling Mills.
Cold Rolling :
Rolling of steel (normally flat products) below the recrystallisation temperature of steel (normally at room temperature) to produce cold rolled sheets /strips /coils. Mills used for the purpose are called Cold Rolling Mills.
2Hi/4 Hi/6 Hi/20 Hi Mills :
Rolling Mills are classified as 2-High / 2 Hi, 4 Hi and so on depending on Number of Rolls used in the arrangement/configuration of rolls in single stand. For example, a 2 Hi mill consist of 2 rolls one above the other known as upper roll and the lower roll. In a 4 Hi mill, there are 4 rolls in a stand—2 upper rolls one above the other and 2 lower rolls one above the other.
Thermo Mechanically Treated Bars that are having hard outer core and soft inner core is known as TMT Bar.
Thermo Mechanical Treatment involves three steps that are:
- Quenching
- Self Tempering
- Atmospheric Cooling
In first step of TMT Bar manufacturing process the steel bars passes through the rolling mill. On the next step the steel bars again passes through the Thermex water cooling system. During the time it passes through the Thermex water cooling system due to optimized water pressure outer core of the TMT Bar becomes tough and durable.
During the next step Atmospheric cooling TMT Rebar inner core remain softer and that is why TMT Rebar are highly ductile. It has strong outer core and soft inner core and slowly it turns into Ferrite-Pearlite Mass. For this unique cold stress technology TMT bars are super ductile in nature and widely accepted for all type of construction purposes.
TMT Rebars are Corrosion Resistant, Fire Resistant. For high ductility TMT Bars can exchange extra energy during an earthquake and that is why it protects every kind of structure during the earthquake.
Shyam Stel’s flexiSTRONG TMT Rebars comes with greater tensile strength. For higher elonagtion it can bend/re-bend when it is required for all type of construction. For Earthquake prone zones it is necessary to choose TMT Bars that are highly ductile. Shyam Steel’s fe 500D TMT Bars are widely accepted for being the best in quality in India for all type of construction purposes. Shyam Steel’s best TMT Rebars are highly resistant to fire and that is why it makes safe the building from fire hazards. For higher elongation flexiSTRONG TMT Bars bond makes the stronger bond in RCC therefore, it makes the structure strong, durable and increases its longevity.
MISCELLANEOUS TERMS:
Steel Melting Scrap :
Steel waste/scrap not usable as such in its existing form which are further re-melted to produce liquid steel to produce various products. Depending on their form/type, they are classified as Heavy Melting Scrap, Light Melting Scrap, Turnings/borings etc.
Re-rollable Scrap :
Seconds & defective products, cuttings/end cuttings, used steel products like used rails etc which could be directly used for re-rolling (without resorting to re-melting) into finished products for specified applications. These are substitutes of steel billets /pencil ingots. Ship breaking generates substantial quantity of re-rollable steel scrap.
Integrated Steel Plants :
Steel plants using iron ore as the basic raw material for production of crude steel which is further rolled into finished shapes in-house. Conventionally, these plants have captive coke ovens also and the sensible heat of the outgoing gases from iron/coke making are utilised as fuel for various applications. It therefore, includes units with in-house coke making (optional), iron making followed by production of liquid steel & crude steel and finished steel. So all ISPs adopting BF- BOF route and Major producers adopting Corex-BOF or DRI-EAFor MBF-EOF technology would technically, fall under this category.
Mini Steel Plants :
Conventionally, EAF/IF based steel plants with/ without captive rolling mills were covered under this category. However, now all steel plants (based on any technology) of capacity upto 5 lakh tpa are covered under this category.
Primary Steel Producers :
Steel (crude and/or finished steel) producers using iron ore as the basic raw material/input. It therefore, includes in-house iron making followed by production of liquid steel & crude steel with/without in-house rolling. So, all ISPs adopting BF- BOF route and Major producers adopting Corex – BOF or DRI-EAF or MBF-EOF technology would fall under this category.
Hot Rolling :
Rolling of steel at above the recrystallisation temperature of steel (normally above 1000 C) to produce Hot Rolled Long products/Flat Products from semis. Ingots are also hot rolled to get semis. At times blloms are also hot rolled to produce billets. Rolling Mills used for hot rolling are known as Hot Rolling Mills.
Cold Rolling :
Rolling of steel (normally flat products) below the recrystallisation temperature of steel (normally at room temperature) to produce cold rolled sheets /strips /coils. Mills used for the purpose are called Cold Rolling Mills.
2Hi/4 Hi/6 Hi/20 Hi Mills :
Rolling Mills are classified as 2-High / 2 Hi, 4 Hi and so on depending on Number of Rolls used in the arrangement/configuration of rolls in single stand. For example, a 2 Hi mill consist of 2 rolls one above the other known as upper roll and the lower roll. In a 4 Hi mill, there are 4 rolls in a stand—2 upper rolls one above the other and 2 lower rolls one above the other.
Thermo-mechanical Treatment
Thermo mechanical treatment is an advance level innovation in steel industry. It refers to simultaneous application of heating and cooling to steel. TMT Bars undergo thermo mechanical treatment thus it’s extremely ductile and it has higher tensile strength.
Superior Ductility
TMT Bars are extremely ductile. That is why it can be used for every shape.
Superior Bendability
For ductility it can bend for any shape without losing its strength.
Earthquake Resistant
During Thermo mechanical treatment it becomes ferrite pearlite structure, which means it becomes strong in its outer core and inner part of it remains soft. For this it can exchange extra energy during an earthquake. TMT Bars with its strength & flexibility makes every construction Earthquake Resistant thus everlasting. It prevents uprooting any structure during an earthquake.
Corrosion Resistant
TMT Bars undergo controlled water cooling process that resists formation of coarse carbides. These unrefined carbon that referred as coarse carbides are the main reason that develop the corrosion. In TMT Bars there is no surface stress that another reason for TMT Bars to be corrosion resistant.
Fire Resistant
During the process of manufacturing TMT Bars becomes highly resistant to Fire. For its Thermal Stability It can resist up to 600 Degree Celsius of heat. TMT Bars are highly resistant to fire.
Great Strength to RCC
Across the TMT Bars external ribs that are spread across its external edge gives an additional advantage to bond it with RCC. In RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) TMT bars are the component that provides strength to the structure and makes it long lasting.
Environment friendly
TMT Bars saves upto 17% of steel than other type of steel bar. Along with its superior strength & ductility TMT Bars are cost effective. Also TMT Bars easy to transport because these can be easily bend as per the requirement. The weight of TMT Bar is less than other type of Steel Bars.
Saves Time
For easy Bendability it can be used for all type of structures. It saves time because TMT Bars can easily bend or restructured according to the requirement at construction site.

