Which Assets Cannot Be Depreciated? Understanding Non-Depreciable Assets

To have a better understanding, look at the kind of assets that depreciate and the ones that will depreciate over time. The IRS has strict guidelines regarding which assets cannot be depreciated and which ones can have their value deducted. Let’s break down what assets are depreciable as well as assets the IRS won’t allow you to recover the cost for. Financial Assets, unlike most Real Assets, cannot be depreciated as they do not automatically lose value and are held as an investment and not for income generation. Depreciable Assets are those which lose value over time, and which are held for the long term.
Capitalizing Website Development Costs: Financial Implications Explained
- By navigating through the complexities of non-depreciable assets, businesses and financial enthusiasts alike unlock a deeper understanding of asset valuation and strategic management.
- The decline in value is because the asset no longer has any use in the current economy.
- Since non-depreciable assets like land and art remain on the balance sheet at their historical or revalued cost without being reduced by depreciation, the total asset base remains higher.
- In taxation, these assets are not subject to periodic deductions in the form of depreciation.
- Its value may fluctuate based on market conditions, but it does not diminish due to usage or the passage of time.
Rather than expensing the total cost of an asset in the year of purchase, depreciation spreads this expense over its useful life, aligning the cost with the revenue generated from it. Although a business can use physical properties such as buildings, vehicles, furniture, and equipment for several years, they do not last forever. Accountants and financial professionals are crucial in ensuring accurate asset classification through diligent record-keeping, adherence to accounting depreciable assets standards, and asset characteristics analysis. Investments and securities represent another category of assets exempt from depreciation. These financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, derive value from market fluctuations and economic conditions rather than physical deterioration.

Examples of assets that do not depreciate
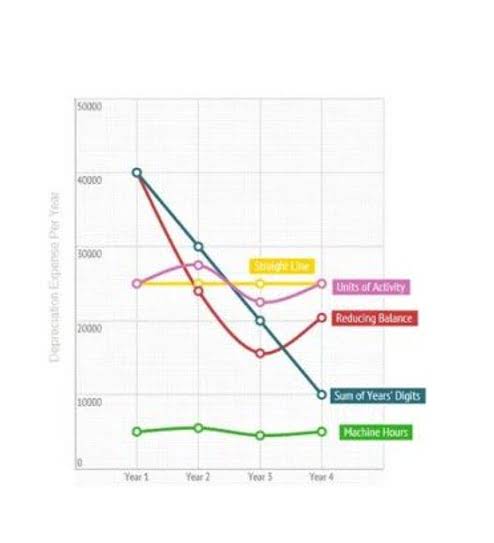
This unique characteristic of land distinguishes it from other depreciable properties, making it a stable asset in terms of value retention or potential growth. Throughout this article, we’ve unraveled the complexities of non-depreciable assets, shedding light on their characteristics, implications, and alternative accounting treatments. Each asset category, from land holdings to investments and inventory, presents unique challenges and considerations for accurate financial reporting and strategic decision-making. Depreciation involves several key steps, including determining an asset’s useful life and salvage value. Various depreciation methods exist, including straight-line, declining balance, and units of production, each suited to different asset types and business requirements. Depreciation expenses are recorded on the income statement, reducing net income and taxable income, while accumulated depreciation is recorded on the Bookkeeping for Painters balance sheet, offsetting the asset’s original cost.

Try for free for 30 days. Free forever up to 10 assets
Depreciation allocates the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives, reflecting wear and tear. Non-depreciable assets play a crucial role in the financial landscape of businesses, representing long-term investments and strategic assets that balance sheet contribute to growth and value creation. Moreover, transparent and accurate financial reporting enhances stakeholder confidence and trust, fostering long-term success and sustainability for businesses. Understanding the concept of depreciable assets, both tangible and intangible, is essential for effective financial management. Moreover, transparent and accurate financial statements enhance stakeholder confidence and trust, fostering long-term success and sustainability for businesses.
Among these concepts, non-depreciable assets stand out as a category that does not diminish in value due to usage or time. Their treatment within a company’s books and tax filings has significant implications. Non-depreciable assets typically include land, certain intangible assets (like goodwill), and items that do not lose value over time because of use or obsolescence. These assets retain their original value and thus do not qualify for depreciation. Understanding the tax implications related to depreciation and non-depreciable assets is essential for sound financial management.
Depreciation In Cost Accounting: What Is It And Why Does It Matter?
In the balance sheet, accumulated depreciation and amortization are subtracted from the gross asset value, presenting the net book value. Companies must consistently apply these accounting methods to ensure accurate reporting to stakeholders. This clarity supports informed decision-making and compliance with regulatory standards, as detailed in authoritative resources such as the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). While this article provides valuable insights into non-depreciable assets, the complexities of asset classification may require additional guidance from accounting professionals. By spreading the expense over the asset’s lifespan, businesses can achieve a more accurate financial picture. This process affects the balance sheet and the income statement, touching upon a firm’s net income and asset value.
Understanding Non-Depreciable Assets

For example, the initial cost of depreciable assets decreases taxable income each year they are in use. Businesses should track depreciation carefully to maximize available tax deductions. Depreciable assets include all tangible fixed assets of a business that can be seen and touched such as buildings, machinery, vehicles, and equipment. Fixed asset depreciation is an accounting technique employed to distribute the cost of tangible, long-term …
